3 Future of Work Predictions for 2024 and Beyond - Through the Looking Glass
After much back-and-forth on work models, bold ultimatums from employers and staunch resistance from workers, European businesses are in the process of codifying different ways of where, how, when, and why we work. One of the many reasons for this change is the speed with which technology, especially artificial intelligence and GenAI, have made it possible to work equally well in varying, flexible work models.
The downside of this rapid technology development has been that European organizations simply cannot hire enough workers with current or deep skills – both technical and human. Do you manage highly distributed teams performing complex and interdependent tasks? Certainly not easy. Finding employees trained sufficiently well to safely transition to the use of Gen AI solutions? Not easy either.
Enter the promise of automation and in particular the ability of AI and Gen AI tools to both facilitate repetitive tasks like coding, data entry, research, and content creation but also to amplify the effectiveness of learning in the flow of work and secure company assets.
The following 3 predictions are examples of what work in Europe might look like in the next five years, considering the areas of work personalization, skills development and the impact of climate change on office design.
Future of Work Predictions for 2024 and Beyond
- Prediction 1: 60% of Large Businesses will upgrade hardware and software technologies to increase worker retention with personalized work experiences and enhanced collaboration by 2025.
Rapidly evolving technologies and work methods are forcing companies to upgrade hardware and implement new software technologies that support better employee experiences, personalization and improved collaboration.
Collaboration apps are becoming more visual and continue to develop features unlike multiplayer games that enable a more personalized view of work and teams, better targeting of projects, and hands-on collaboration apps. Meetings and other work resources, including collaboration resources (workflow, meetings, new document formats, etc.) are translated and transcribed in real time, captured, analyzed and exploited by other integrated business data sources. The results enable faster and more personalized decisions and collaboration, including summaries using generative AI. AI solutions are gradually increasing the ways people consume content and data, and AI itself will become a digital collaborator.
- Prediction 2: Enterprises will leverage personalized technology skills development to drive $1T in productivity gains by 2026, enabled by GenAI and automation everywhere.
As the development and use of technology in everyday work environments becomes more complex, organizations struggle to find experts for programming, security, architecture, operations, management and many other roles. IDC data from 2023 shows that 43 % percent of organizations lack the capability support needed to successfully implement automation.
One of the reasons Gen AI adoption and experimentation has grown so rapidly is that everyday workers can see its immediate value. As new jobs come online due to new automation requirements and workers learn new skills, Gen AI is being incorporated into tools that create employee training. Workers with entry-level skills can better target individual learning needs based on the speed with which Gen AI can generate code, summarize data, and create first-draft multimedia products. This customized approach ensures that people (including IT staff) receive the most appropriate training, optimizing efforts to increase their skills and competencies as jobs evolve, plus the need to program GenAI applications themselves.
- Prediction 3: By 2028, organizations will invest in office climate havens, using asset-based/renewable energy to defray 30% of their ongoing operating costs.
It is not just work patterns that are rapidly changing. The environment we live and work in is rapidly changing too. As uncontrolled wildfires, climate change and extreme weather events become more common in Europe, the consequences are affecting human health and the ability to work effectively. Sustainability measures are no longer considered optional as organizations worldwide recognize them as necessary components of strategic planning and sustainable operational excellence.
In future, progressive companies will adopt a combination of innovative building design, digital twins, robotics and integrated climate systems to create climate havens where workers and their families can both find relief and focus on work. Unfortunately, simply rebuilding existing buildings with AI or robotics adds energy demand to an already struggling European energy infrastructure.
Companies that invest heavily in asset-based energy (hydro/tidal, geothermal, solar and wind) on-site in their climate havens, support both their operating costs and potentially create a secondary revenue stream when they feed electricity back into the grid. This is reversing the long-term trend of digital organizations threatening their local communities through excessive power usage, while improving community relations, employee retention and talent recruitment.
All the above predictions have much in common – they seek to better understand the intersection of technology and human behavior. Science fiction predicts dystopian visions of mechanized and artificially controlled societies where human efficacy is threatened. IDC far from that point of view, but we also see how the concerns raised by new technologies such as Gen AI can play a big role in hindering adoption—for better or for worse.
Organizational leaders must invest time and money in the strategic planning for the adoption of AI and GenAI technologies, as well as the new roles and ways of working they create. This is not just a technology issue that affects computing, security, hardware, infrastructure, and integration requirements. It is also a human issue that must be addressed employee empowerment through skill development and the development of appropriate, re-imagined career paths.
For more information on the impact of Automation on the European Future of Work, please access the following resources:
- Five Ways to Unlock a Purposeful, Automated Future of Work in EMEA – watch now
- IDC EMEA FutureScape 2024: Reimagining an AI Everywhere Digital Future- https://goto.webcasts.com/starthere.jsp?ei=1635711&tp_key=4edfcb9432&sti=website
Ready for NRF 2024: 10 Imperatives for Success in Retail
NRF24 Retail’s Big Show in New York City is fast approaching, and we, IDC Retail Insights will be there. We cannot wait to talk with retailers, technology companies, and industry experts, share our views and learn more about what matters for the industry in 2024 and beyond.
As we prepare for the event, let’s summarize the critical technological imperatives that retailers must embrace to thrive in today’s ever-evolving business environment. Our insights are drawn from IDC Retail Insights’ Global Retail Survey 2023, where over 800 retailers worldwide shared their strategic priorities. Let’s dive into it!
Multilevel Loyalty Strategy for a Greater Retail and Customer Experience
We predict that “by 2024, 40% of Retailers Will Adopt a Multilevel Loyalty Strategy, Leveraging a Unified View of the Customer, to Increase Retention Rate by 20% and Net Promoter Score by 35%”. Retailers worldwide are on the brink of customer loyalty revolution, with a staggering 35% gearing up to unveil cutting-edge multilevel programs within just three years, as revealed by IDC’s 2023 Global Retail Survey.
The once-reliable methods like points and promotions are losing their edge, lacking the spark needed to captivate customers. Now, in an era where privacy regulations tighten and accessing third-party data becomes limited, the game-changer lies in collecting firsthand customer data—it’s the cornerstone of tomorrow’s success.
But the game is evolving, and the retail world is diving headfirst into the realm of immersive tech. By embracing this tech-savvy frontier, retailers can elevate loyalty strategies, crafting experiences finely tuned for the ever-evolving Alpha and Gen Z consumers.
Brands like Ralph Lauren and Lacoste are venturing into Web3 for exclusive immersive experiences and community building.
The real challenge is about seamlessly delivering these immersive experiences across every retail touchpoint, navigating a landscape growing more complex by the day. That’s why empowering workforce with digital tools isn’t just essential; it’s a key differentiator for maintaining contextualized customer experiences.
Meanwhile, in the hospitality sector, a digital revolution is reshaping the guest experience, demanding personalized, predictive experiences despite ongoing labour shortages. This calls for a strategic fusion of systems and capabilities, a dynamic approach to cater to the digital-driven needs of today’s guests.
Investing in Technology to Deliver Efficiencies and Effectiveness in the Omnichannel Customer Journey
Retailers are navigating challenging a business environment and are under pressure to increase revenue and reduce costs. According to our IDC Global Retail Survey, while customer experience is at the top of retailers’ concerns, increasing operational efficiency is the second most important business priority for retailers.
This is mainly due to the greater complexity of the business environment the industry faces.
Let’s consider, for example, the role of brick-and-mortar in today’s omnichannel operations. The physical store is the pillar of retail operations today, but it must be connected and fully integrated with digital operations to play its role as the centrepiece of the customer journey.
One strategic imperative for retailers is investing in in-store Technology, such as AI, Computer Vision, and IoT, to digitize, automate, and streamline the omnichannel experience in-store.
While retailers are navigating challenging territories and need to do more with less, they haven’t stopped investing in technology. Top investment areas in 2024 include physical infrastructure, cloud, and managed services.
Therefore, another digital transformation imperative is investing in IT Infrastructure, including network infrastructure to connect the physical store and rethink cloud and edge balance to provide a seamless omnichannel experience.
A transformation imperative that should not be overlooked to streamline the efficiency of retailers’ operations is linked to the importance of embracing a best-of-breed Retail Commerce Platform. Retailers are investing in modular and headless platforms, to move towards composable architectures that match the needs of modern omnichannel retail.
As we can see, retailers should be laser-focused on the technological imperatives that make omnichannel operations more efficient and in turn generate better omnichannel customer experience.
AI and Augmented Reality for Customer Experience
In today’s landscape, AI is everywhere as it’s revolutionizing how consumer brands approach customer experiences. This shift places a heightened emphasis on human-centric approaches, especially as AI and GenAI streamlines routine tasks.
In this augmented context, organizations are placing a premium on customer empathy, trust, and privacy. However, this requires a fundamental leadership’s cultural shift and a business transformation, detached from traditional hierarchies towards flatter structures, identifying shared metrics, and nurturing a collaborative culture where innovation thrives.
Retailers growing attention to and investment in advanced analytics, AI, machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP) are unlocking and demonstrating the potential of generative AI (GenAI). It is a point of no return, where retailers are shifting from being merely data-rich to strategically data-driven organizations.
Omnipresence across different channels, such as social media networks, marketplaces, ecommerce, in combination with personalized engagements allow retailers to extract real-time value from every interaction. AI’s impact on CX personalization is profound, evolving from static segments to real-time, context-driven experiences.
The depth of coherent customer data leverages the integration of AI and ML analytics, notably in predictive product recommendations. Our IDC’s 2024 Retail Predictions say that “by 2028, 50% of retailers will offer AI-enabled contextualized recommendations to enhance customer engagement, increasing real-time interactions by 30% and overall conversion rate by 20%”.
These AI algorithms amplify omni-channel strategies, empowering both store associates and digital agents for seamless customer engagements as well as contextualized marketing and merchandising. AI isn’t merely a buzzword; it’s a game-changer. Particularly, it’s reshaping new revenue streams, such as Retail Media Networks, facilitating and powering orchestration across interconnected systems, aiming to seamlessly handle pricing, inventory, forecasting, planning, and maintain consistency across channels and partners.
Importance of the Supply Chain on the Customer Journey and Sustainability
Retail logistics have seen a few challenges in recent years, including disrupted sourcing streams and workforce shortages, but supply chains have started to readjust. Despite things getting better, retailers are preparing for the future by anticipating challenges like those experienced in the recent past, and now investing in making the Supply Chain even more resilient through greater automation and data insight has become a digital transformation imperative.
The primary reason for investing in the supply chain is to increase efficiency and improve product availability, resulting in a better omnichannel customer experience. Sustainability is also a big factor in retailers’ strategic imperatives related to improving the efficiency of the supply chain.
Fortunately, these two objectives—efficiency and sustainability—are not in conflict with each other. Investing in supply chain efficiency has the potential to reduce costs, improve customer experience, and make operations more sustainable.
Retailers are taking a proactive approach to address the challenges of the future. By investing in supply chain resilience, they are ensuring that they can continue to provide the best possible customer experience while also being mindful of the environment.
Let’s Meet at NRF!
As we anticipate key themes for IT vendors and retailers in 2024, we expect these 10 Imperatives for Success to be prominent topics in our conversations at NRF in January. If you’re attending NRF, reach out to us to arrange a meeting or visit our booth at number #1032.
We look forward to meeting you there!
IDC’s Key Takeaways from Enlit Europe 2023
This year’s Enlit Europe, which took place between November 28 and November 30 in Paris, attracted almost 12,000 visitors,700 exhibitors from 100 countries and 500 speakers, — proving once again to be a reference point for the European (if not worldwide) utility sector.
Sessions on the energy transition (energy efficiency, electrification and decarbonization), flexibility, and digitalization, as well as numerous hub sessions, provided a great opportunity for knowledge sharing during the three-day event. Here are our key takeaways from discussions and debates with technology providers and utilities.
Among the conversations with various utility leaders, three key themes emerged that outline the direction in which this industry is moving.
- Flexibility at the heart of energy transformation. One of the dominant conversations that continued this year at Enlit is the growing criticality of flexibility for the utility industry. With increasing renewable energy sources and the need to integrate distributed energy resources more effectively, utilities are increasingly focusing on operational flexibility. Additionally, booming electrification requires demand flexibility to mitigate the impact of the energy transition on grids, which are the invisible enabler of it all. Industry representatives stressed the importance of investing in technologies and systems that enable more dynamic grid management, ensuring more efficient and sustainable energy distribution and consumption.
- The imperative of marketing. Another interesting aspect that emerged during the event was the growing success of utilities that understand the value of marketing, to change customers’ perception of their company and the industry as a whole, while improving their relationship with consumers. Utilities that have invested in understanding consumer needs and have built strong brands are reaping the benefits. Utilities are at the heart of a transformation that impacts everyone and will set the stage for the next generations, if done right and marketed well, companies can turn misconception of the industry on its head, leading to newfound success.
- What about Generative AI? Despite growing interest over the last year, the topic of GenAI was not as apparent as we would have expected. Discussions we had were more focused on the benefits of horizontal applications of GenAI and very rarely on industry specific use cases that utilities should be digging into. Currently, the discourse on GenAI tends to be more high-level than practical, with utilities trying to figure out how to integrate this technology effectively into their daily operations. The largely uncharted territory of GenAI also raised additional conversations around artificial intelligence and machine learning overall and the untapped potential that still exists. And it all came back to the topic of “data” … the quality of the data, the frequency of the data, the amount of data, etc. The challenge now is for utilities to translate high-level discussions into concrete and practical action, successfully addressing industry challenges and capitalizing on emerging opportunities. And for this they need the help of their peers and the technology ecosystem that surrounds them.
Overall, it was positive to see an Enlit returning to its pre-COVID bustle, with a diverse pool of companies exhibiting on the floor, both from a software and a hardware perspective. Let’s hope the onsite enthusiasm trickles into utilities daily activities fostering more drive to the energy transition.
Here’s to quickening progress in 2024 to be discussed when we meet in Milan at next year’s Enlit Europe.
For more of our coverage on the energy market, visit our website.
The Dawn of Mass Adoption or AR
The Dawn of Augmented Reality
The recent metaverse hype catalyzed discussions around augmented reality. However, AR is not a new concept.
The first mention in science-fiction of the concept of augmented reality occurred already in the early 20th century. But only thanks to the incredibly fast technological advancements of the past decade did augmented reality become a science-based reality.
Indeed, the latest advancements in augmented and mixed reality technologies like Apple’s new headset are stirring a lot of interest. The past decade witnessed the emergence of the first modern augmented reality devices, starting with Google Glass released in 2012, the first Microsoft HoloLens or Magic Leap One headsets.
Until recently, the costs of augmented reality were substantial, but today things have changed and augmented reality is becoming available to businesses and consumers.
AR is Gaining Momentum
When Google Glass – the first augmented reality consumer-oriented device – was unveiled in 2012, it was supposed to revolutionize the wearables world. However, its clunky design, limited number of functionalities and its steep price of $1,500 did not convince the smart glasses consumer niche.
While Google Glass no longer exists, the technology lives on within the products that succeeded it. Other companies such as Vuzix or Microsoft have since expanded the niche in a way Google Glass was not able to.
While virtual reality is already enjoying much popularity in the market, especially in the consumer segment, augmented reality is slowly unveiling its potential. In Europe, the AR market reached $ 0.8 billion last year and since then is expected to almost triple by 2027 growing at a 21,7% five-year CAGR. As new use cases emerge, we will see a strong adoption curve of AR in the coming years.
The Pioneers in AR Implementation
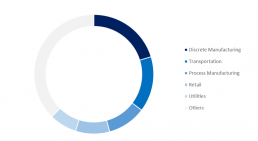
The use of AR is increasingly common in the commercial sector. It is largely deployed in discrete and process manufacturing industry, in transportation and in retail. These four industries together absorb 55.0% of AR-related spending in Europe in 2023.
Augmented reality has revolutionized the way manufacturers design, produce, and distribute products. Using AR, Intel has transformed its operations in its semiconductor fabrication facility in Ireland, one of the most advanced manufacturing facilities. Working in the smallest known geometry Intel manufacturing process is extremely complex. Manufacturing technicians use the HoloLens 2 which has become integral to Intel manufacturing processes from maintenance and repair tasks to remote communication and troubleshooting and training.
AR will see a boom in the consumer segment in the next five years, with purchases growing at a 53.6% five-year CAGR. In the commercial space, it is central government to see the most significant increase in AR spending as many European governments have committed to allocate substantial part of their national resilience plans to digitalization projects such as smart cities.
The Benefits of AR for Businesses
AR technology can revolutionize the way we work and live. It enriches the traditional work environment and optimizes business processes while providing significant benefits in terms of safety, efficiency, and productivity.
By allowing virtual objects and real-time information into the physical world, AR can dramatically expand the user’s access to information and performance. In production-driven industries like manufacturing, augmented reality allows us to display every feature of a machine, product, or component, visualize and streamline complex concepts and processes, and provide valuable insight into the operations. Employees can access and apply detailed instructions while they work and make better informed decisions which helps mitigate downtime and reduce errors. This in turn results in overall optimization of processes across the value chain enhancing time and costs efficiencies.
AR helps reduce work-related hazards and improve workplace safety, this is particularly important in the case of industrial organizations that have complex heavy machinery which might be unsafe to operate, or in remote or hard-to-reach locations, where carrying out operations may be time-consuming or dangerous. AR offers the opportunity to identify potential risks in real time or operate remotely.
AR has been shown to be enormously effective in improving the learning curve for the employees. Immersive training is tailored to a particular worker and is more engaging with traditional learning methods leading to increased knowledge retention while reducing training time. European organizations recognize its potential and increasingly allocate a substantial portion of AR-related budget to virtual training. Investments in AR training will grow at a 46.7% CAGR by 2027.
Companies across Europe have long been struggling to find a qualified workforce. The pandemic accelerated digital transformation in organizations which would boost technical progress but would reveal how deepening skills gap creates bottleneck in the transformation.
According to IDC’s Future Enterprise and Resiliency Survey, organizations are seeing delays in digital transformation of more than eight months due to the lack of skills. In the current setting of ageing population and low supply of the talent from universities and professional courses which potentially undermine the technological progress, AR offers a great opportunity for businesses to increase their upskilling and reskilling initiatives from within.
Moreover, augmented reality contributes significantly to enterprises’ efforts towards sustainability. Remote maintenance helps minimize CO2 emissions from travel, contributing to the realization of a low-carbon society and addressing climate change. AR technology allows remote working, helping eliminate inequalities between urban and rural regions, and contribute to the creation of sustainable cities and communities.
Furthermore, remote tools allow employees to achieve higher productivity, contributing to more sustainable economic growth.
Not All Headsets Are Created Equal
Head-mounted displays (HMDs) come in various forms, but all we can divide them between tethered and standalone. Standalone devices are those whose processing is done within the device, usually capable of 3D mapping.
Some examples of standalone devices are Microsoft’s HoloLens 2 and Magic Leap 2. Tethered devices, however, are usually less capable and less expensive. Processing for these devices is done on an external device and most serve simply as an external virtual screen without being capable, by themselves, of 3D mapping. Brands focused in this category include XReal and Rokid.
The AR Market Landscape
The Augmented Reality market has historically been very focused on the commercial segment, with this segment taking approximately 70% of the market, but this is due to change. The dawn of less expensive devices that mainly function as portable screens, as well as new use cases, are bringing this technology to the masses.
If this trend continues, AR HMDs shipments are set to be 45% to consumers by 2027.
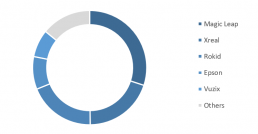
Whilst the more consumer focused VR market is still dominated by a couple of brands (with Meta’s share reaching 60-70%), the AR market is much more fragmented, counting 5 dominant brands. Magic Leap, a high end commercial-industrial focused brand, with devices selling for north of $3.000, is the dominant single brand responsible for about 30% of the AR market. Consumer focused brands that offer “portable screen solutions”, such as Xreal and Rokid take a combined 39% share in 3Q23.
It should also be noted that this market has its peculiarities. Due to the reasons mentioned above, AR headsets are, on average, 5 times more expensive than their VR counterparts, this category’s ASP standing at around $2000. This ASP, along with the still limited use cases, is making these HMDs lagging behind VR, representing 8.1% of the combined ARVR market.
As this technology matures, we should expect a steep decrease in price, as well as substantial share growth of the consumer-focused brands who are proving that this form factor is getting closer to being able to replace laptop screens. When it comes to XR technologies, AR is clearly in a good position to become the fastest growing category.
The Future of AR
As mentioned previously, AR technologies, albeit currently niche, are becoming an important part of many companies’ workflows. Remote collaboration is made easier and seamless; high-fidelity pass-throughs can make digital models come to life and discard expensive physical ones. Handsfree AR screens can make specialist trips for maintenance work unnecessary, design processes are streamlined and made cheaper, as well as training and many other cases. This is what is currently possible with today’s technology, but these are still bulky, expensive, or lacking in features.
It is arguable that one of the most interesting developments in the horizon of technology is the evolution of AR. As breakthroughs are made in the AR space, these devices will become lighter smaller, and more affordable enabling access to a broader range of users, from professional across diverse fields to everyday consumers. If we can visualize a future in which HMDs resemble ordinary eyewear, we start imagining a future where individuals can seamlessly blend digital information with their surroundings.
Education serves a notable example of how we can take advantage of these advancements. Students and researchers will be able to interact with 3D models of anything, from the smallest cell to the entirety of the solar system. Field trips to historical landmarks, or to witness rare scientific phenomena will all be possible from the comfort of the classroom. This will increase retention and comprehension.
Accuracy and efficiency in vital sectors such as healthcare will also be improved to a great extent. Surgeons equipped with AR devices will have access to real-time data visualization during procedures and greater detail in the visualization of internal organs. Augmented reality will also allow patients to have therapy sessions, or to manage chronic conditions from their own home, providing more comfort to the patient and reducing the strain on the health services.
Moreover, entertainment will reach new heights with AR. Imagine watching sports with real-time statistics overlaid on the field or experiencing movies as immersive 3D adventures in your living room.
Whether for work, education, healthcare, or entertainment, as AR becomes more feature-rich and fashionable, the possibilities become limitless. Augmented reality is poised to reshape our perception of what technology is and how we use it to interact with the world around us. The future of AR is not a distant dream but a rapidly approaching reality.