The Dawn of Augmented Reality
The recent metaverse hype catalyzed discussions around augmented reality. However, AR is not a new concept.
The first mention in science-fiction of the concept of augmented reality occurred already in the early 20th century. But only thanks to the incredibly fast technological advancements of the past decade did augmented reality become a science-based reality.
Indeed, the latest advancements in augmented and mixed reality technologies like Apple’s new headset are stirring a lot of interest. The past decade witnessed the emergence of the first modern augmented reality devices, starting with Google Glass released in 2012, the first Microsoft HoloLens or Magic Leap One headsets.
Until recently, the costs of augmented reality were substantial, but today things have changed and augmented reality is becoming available to businesses and consumers.
AR is Gaining Momentum
When Google Glass – the first augmented reality consumer-oriented device – was unveiled in 2012, it was supposed to revolutionize the wearables world. However, its clunky design, limited number of functionalities and its steep price of $1,500 did not convince the smart glasses consumer niche.
While Google Glass no longer exists, the technology lives on within the products that succeeded it. Other companies such as Vuzix or Microsoft have since expanded the niche in a way Google Glass was not able to.
While virtual reality is already enjoying much popularity in the market, especially in the consumer segment, augmented reality is slowly unveiling its potential. In Europe, the AR market reached $ 0.8 billion last year and since then is expected to almost triple by 2027 growing at a 21,7% five-year CAGR. As new use cases emerge, we will see a strong adoption curve of AR in the coming years.
The Pioneers in AR Implementation
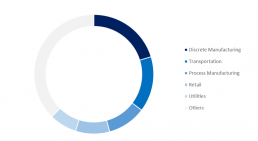
The use of AR is increasingly common in the commercial sector. It is largely deployed in discrete and process manufacturing industry, in transportation and in retail. These four industries together absorb 55.0% of AR-related spending in Europe in 2023.
Augmented reality has revolutionized the way manufacturers design, produce, and distribute products. Using AR, Intel has transformed its operations in its semiconductor fabrication facility in Ireland, one of the most advanced manufacturing facilities. Working in the smallest known geometry Intel manufacturing process is extremely complex. Manufacturing technicians use the HoloLens 2 which has become integral to Intel manufacturing processes from maintenance and repair tasks to remote communication and troubleshooting and training.
AR will see a boom in the consumer segment in the next five years, with purchases growing at a 53.6% five-year CAGR. In the commercial space, it is central government to see the most significant increase in AR spending as many European governments have committed to allocate substantial part of their national resilience plans to digitalization projects such as smart cities.
The Benefits of AR for Businesses
AR technology can revolutionize the way we work and live. It enriches the traditional work environment and optimizes business processes while providing significant benefits in terms of safety, efficiency, and productivity.
By allowing virtual objects and real-time information into the physical world, AR can dramatically expand the user’s access to information and performance. In production-driven industries like manufacturing, augmented reality allows us to display every feature of a machine, product, or component, visualize and streamline complex concepts and processes, and provide valuable insight into the operations. Employees can access and apply detailed instructions while they work and make better informed decisions which helps mitigate downtime and reduce errors. This in turn results in overall optimization of processes across the value chain enhancing time and costs efficiencies.
AR helps reduce work-related hazards and improve workplace safety, this is particularly important in the case of industrial organizations that have complex heavy machinery which might be unsafe to operate, or in remote or hard-to-reach locations, where carrying out operations may be time-consuming or dangerous. AR offers the opportunity to identify potential risks in real time or operate remotely.
AR has been shown to be enormously effective in improving the learning curve for the employees. Immersive training is tailored to a particular worker and is more engaging with traditional learning methods leading to increased knowledge retention while reducing training time. European organizations recognize its potential and increasingly allocate a substantial portion of AR-related budget to virtual training. Investments in AR training will grow at a 46.7% CAGR by 2027.
Companies across Europe have long been struggling to find a qualified workforce. The pandemic accelerated digital transformation in organizations which would boost technical progress but would reveal how deepening skills gap creates bottleneck in the transformation.
According to IDC’s Future Enterprise and Resiliency Survey, organizations are seeing delays in digital transformation of more than eight months due to the lack of skills. In the current setting of ageing population and low supply of the talent from universities and professional courses which potentially undermine the technological progress, AR offers a great opportunity for businesses to increase their upskilling and reskilling initiatives from within.
Moreover, augmented reality contributes significantly to enterprises’ efforts towards sustainability. Remote maintenance helps minimize CO2 emissions from travel, contributing to the realization of a low-carbon society and addressing climate change. AR technology allows remote working, helping eliminate inequalities between urban and rural regions, and contribute to the creation of sustainable cities and communities.
Furthermore, remote tools allow employees to achieve higher productivity, contributing to more sustainable economic growth.
Not All Headsets Are Created Equal
Head-mounted displays (HMDs) come in various forms, but all we can divide them between tethered and standalone. Standalone devices are those whose processing is done within the device, usually capable of 3D mapping.
Some examples of standalone devices are Microsoft’s HoloLens 2 and Magic Leap 2. Tethered devices, however, are usually less capable and less expensive. Processing for these devices is done on an external device and most serve simply as an external virtual screen without being capable, by themselves, of 3D mapping. Brands focused in this category include XReal and Rokid.
The AR Market Landscape
The Augmented Reality market has historically been very focused on the commercial segment, with this segment taking approximately 70% of the market, but this is due to change. The dawn of less expensive devices that mainly function as portable screens, as well as new use cases, are bringing this technology to the masses.
If this trend continues, AR HMDs shipments are set to be 45% to consumers by 2027.
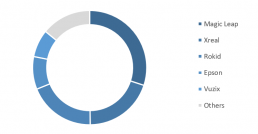
Whilst the more consumer focused VR market is still dominated by a couple of brands (with Meta’s share reaching 60-70%), the AR market is much more fragmented, counting 5 dominant brands. Magic Leap, a high end commercial-industrial focused brand, with devices selling for north of $3.000, is the dominant single brand responsible for about 30% of the AR market. Consumer focused brands that offer “portable screen solutions”, such as Xreal and Rokid take a combined 39% share in 3Q23.
It should also be noted that this market has its peculiarities. Due to the reasons mentioned above, AR headsets are, on average, 5 times more expensive than their VR counterparts, this category’s ASP standing at around $2000. This ASP, along with the still limited use cases, is making these HMDs lagging behind VR, representing 8.1% of the combined ARVR market.
As this technology matures, we should expect a steep decrease in price, as well as substantial share growth of the consumer-focused brands who are proving that this form factor is getting closer to being able to replace laptop screens. When it comes to XR technologies, AR is clearly in a good position to become the fastest growing category.
The Future of AR
As mentioned previously, AR technologies, albeit currently niche, are becoming an important part of many companies’ workflows. Remote collaboration is made easier and seamless; high-fidelity pass-throughs can make digital models come to life and discard expensive physical ones. Handsfree AR screens can make specialist trips for maintenance work unnecessary, design processes are streamlined and made cheaper, as well as training and many other cases. This is what is currently possible with today’s technology, but these are still bulky, expensive, or lacking in features.
It is arguable that one of the most interesting developments in the horizon of technology is the evolution of AR. As breakthroughs are made in the AR space, these devices will become lighter smaller, and more affordable enabling access to a broader range of users, from professional across diverse fields to everyday consumers. If we can visualize a future in which HMDs resemble ordinary eyewear, we start imagining a future where individuals can seamlessly blend digital information with their surroundings.
Education serves a notable example of how we can take advantage of these advancements. Students and researchers will be able to interact with 3D models of anything, from the smallest cell to the entirety of the solar system. Field trips to historical landmarks, or to witness rare scientific phenomena will all be possible from the comfort of the classroom. This will increase retention and comprehension.
Accuracy and efficiency in vital sectors such as healthcare will also be improved to a great extent. Surgeons equipped with AR devices will have access to real-time data visualization during procedures and greater detail in the visualization of internal organs. Augmented reality will also allow patients to have therapy sessions, or to manage chronic conditions from their own home, providing more comfort to the patient and reducing the strain on the health services.
Moreover, entertainment will reach new heights with AR. Imagine watching sports with real-time statistics overlaid on the field or experiencing movies as immersive 3D adventures in your living room.
Whether for work, education, healthcare, or entertainment, as AR becomes more feature-rich and fashionable, the possibilities become limitless. Augmented reality is poised to reshape our perception of what technology is and how we use it to interact with the world around us. The future of AR is not a distant dream but a rapidly approaching reality.