The ongoing wave of disruptions globally has underlined the importance of digital transformation (DX) in manufacturing organisations. It was evident during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic that digitally mature companies fared better in responding to disruptions than their peers with lower levels of digitalisation.
As the manufacturing sector globally faces continued uncertainty — with soaring inflation levels, energy crisis, raw material and component shortages, skills shortages and other supply chain disruptions — climbing the smart manufacturing maturity ladder is vital to ensure business continuity and make production more resilient in the long term.
In the same way, the dynamic business environment is providing opportunities that drive manufacturers to digitally transform their production. For instance, the push towards environmental sustainability and agile/remote production is an important catalyst for organisations to accelerate their smart manufacturing initiatives.
Smart manufacturing is defined as the continuous process by which enterprises leverage cyberphysical convergence and digital skills to develop the production capabilities to compete in the modern economy. It encompasses intelligent machines from machines and tools to collaborative robots, emerging sets of business applications enabled by cloud and industrial Internet of Things (IoT), technology enablers such as digital twins and AI, and other rapidly evolving technologies and standards that support smart production.
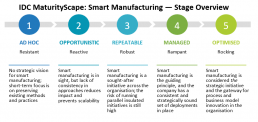
Assessing Your Factory’s Digital Maturity with the IDC Smart Manufacturing MaturityScape
The IDC Smart Manufacturing MaturityScape provides a framework for executive leadership, IT and production managers to identify the stages, critical measures, outcomes and actions required for organisations to evaluate and evolve their digital factory strategies. It offers a model to help companies know where they stand and take steps to drive their progress.
There are 5 stages in the IDC MaturityScape, from the least mature and capable Ad Hoc stage to the most mature and capable Optimised stage. At higher levels of maturity, smart manufacturing is a companywide strategic initiative and a major driver of competitiveness and innovation.
At this Optimised stage, companies recognise that mastering their factory floor processes enables them to become proactively disruptive in their market segments, both in delivering cutting-edge products and leveraging transformative business models that entail demand-driven manufacturing and agile production processes.
Addressing Challenges and Staying Ahead of the Game
While the benefits of digital transformation are immense, many companies face roadblocks and struggle to reach higher levels of smart manufacturing. Organisations need to have executives and all relevant stakeholders on board and build a culture that supports digital transformation. They also need to figure out how their operations can contribute to making their business model viable in a world of digitally enabled business ecosystems.
Companies at the lower stages of digital maturity must create a sense of urgency in the organisation and make a conscious effort to assess the technology opportunities available on the market and understand how they can be applied in their organisations. As they progress, it’s important to develop a clear road map with clear and measurable goals, and implement organisational and workforce transformation programmes to enable their digital transformation.
Companies at higher stages instead must enable business reinvention by leveraging smart manufacturing initiatives.
Companies at every stage of digital transformation must:
- Empower the workforce by equipping them with necessary skills and capabilities to enable digital transformation. Workers need to feel engaged by knowing what digital transformation means for them and how they can best contribute to its success.
- Focus on customers by ensuring that smart manufacturing initiatives are relevant and ultimately contribute to providing a competitive value proposition.
- Acknowledge that DX is not a one-off stunt but rather a continuous and transformational process to build a transparent and responsive organisation.
Download the IDC MaturityScape Smart Manufacturing 2.0 to assess the state of your organisation’s smart manufacturing maturity across several dimensions and receive further guidance on how to progress and succeed at every stage of the smart manufacturing journey.
IDC’s European Manufacturing Summit 2022 is the perfect opportunity for manufacturing executives to discuss the key trends, challenges and opportunities that are driving smart manufacturing. It will also offer insights into how organisations can thrive and build resilience in an increasingly complex, volatile and disruptive world.
The IDC Manufacturing Insights: Worldwide Smart Manufacturing Strategies advisory service examines key challenges facing manufacturing companies, such as achieving operational excellence, enabling global manufacturing intelligence and ensuring production quality. It provides fact-based research on IT tools, strategies and best practices in manufacturing operations management (MOM) to meet business challenges, covering the entire spectrum of operational processes from digital factory and production scheduling through manufacturing execution and plant automation to asset management and plant sustainability.