Why Attracting and Keeping Employees Remain Difficult in Europe in 2023
In 2022, the ability to attract and retain talent was the #1 internal CEO concern worldwide according to the Conference Board CEO survey after a booming 2021. Fast-forward 12 months, the environment is different due to layoffs in the tech and financial services sector, inflationary pressures, and the looming recession.
However, in the Conference Board CEO survey for 2023, the ability to attract and retain talent remains the #1 internal CEO concern worldwide.
This CEO expectations of a continuous tight labor market in Europe and elsewhere is supported by data from Eurostat from June 2023. Despite fluctuations mainly related to the Covid-19 pandemic, unemployment appears on a continuous downward trend in the EU, while the EU overall employment rate is on a continuous increase.
The recent wave of layoffs in high tech and related industries – shocking as it was – is unlikely to change this picture. Why? Because it already happened and is on the decrease after peaking around January 2023 for the technology industry and even earlier for other industries, according to Layoffs Tracker.
Our own survey data confirms that the European labor market remains tight. Over half (54%) of software decisionmakers are challenged to find new staff in IDC’s European Enterprise Apps & CX Survey from January 2023 (n = 670). Viewed by industry, recruitment difficulties are present across industries, with signs of some easing of the severe labor shortages that was experienced in retail and hospitality in 2021.
What IDC’s survey data also says is that employee retention pressure has dropped off somewhat in 2023, because of the economic uncertainties and layoffs. In our report, Status of Employee Retention in Europe, based on a survey of 2,785 European employees in March 2022, we found that an alarming one in every four employees on average was actively and voluntarily looking for another job. Some job seekers were forced to look for alternative employment due to relocation or being on a temporary contract (i.e., actively and involuntarily job hunting), and those were excluded.
We made a similar survey in March 2023 of 3,527 employees in Europe. The new survey showed that the proportion of voluntary job seekers had decreased from 24.5% in 2022 to 16.8% in 2023 — a drop of almost 8 percentage points. We asked those that were not actively looking for a new job in terms of why not, and the second and third most popular reasons were most interesting because they referred to the current economic environment, making it “financially sensible to stay” and “hard to find a new job,” respectively.
These concerns appear to be the main reasons why we saw the proportion of voluntary leavers decline from 24% in 2022 to 17% in 2023.
European Organizations Use a Multitude of Coping Strategies to Improve Employee Attraction
Given that the tight labor market is likely to continue for the foreseeable future, what are European organizations doing to get the staff that they need? We asked all software decisionmakers in organizations with some level of recruitment difficulties about their coping strategies.
Interestingly, upskilling and reskilling existing employees was the most popular answer. Educating current employees and redeploying them in new, relevant positions makes sense in many cases.
Existing employees already have valuable knowledge about the organization and industry compared with new hires. One open question is how extensive upskilling/reskilling efforts are required and what learning methods will be needed.
We believe that a significant proportion of the upskilling/reskilling activity will focus on technology and data related skills.
European organizations will also use other methods to make ends meet. The second most popular coping strategy is offering higher salaries, which we see practiced for positions where there is a confined resource pool and limited substitution options. Examples could be a certain trading specialist, a particular medical professional, etc.
Third place was hiring more recruiters and acquiring better recruiting tools, which is a reasonable strategy, especially in organizations where the recruiting function is understaffed and equipped with outdated software and/or processes.
Other popular strategies included widening the spectrum of applicable candidates, lowering criteria, and investing in better branding and candidate marketing.
Three-quarters of organizations deployed a combination of coping strategies. It means that organizations typically see these coping strategies in combination, as opposed as individual silver bullets. Please see Employee Shortage Coping Strategies in Europe (IDC #EUR150726123, June 2023) for more information.
What Are the Upsides from the Point of View of HCM and Payroll Application Vendors in Europe?
The tight labor market and recruiting difficulties among European organizations are in fact sweet music in the ears of many of the software vendors in the HCM space. The solution areas that are best positioned to capitalize on the employee attraction desires and approaches of European organizations are:
- eLearning solutions, learning services, reskilling strategy services. The stated intent to “reskill and upskill” can be achieved by different means, including onsite training, mentoring, and external education courses, learning technologies are also likely to play a key role. IDC believes that the reskilling/upskilling ambitions will trigger investments into more comprehensive eLearning technologies, as opposed to micro learning and social learning approaches.
- Recruiting solutions and services. Vendors of recruiting solutions and HCM suites with strong recruiting modules stand to benefit as do providers of talent acquisition services and recruiting agencies. Investing in such capability is almost mandatory, as the consequence of doing nothing and not being able to attract the required talent can be crippling for an organization.
- Skills mapping, skills management, and skills matching solutions. Upskilling and reskilling is a fine remedy, however, an overview of existing skills and skill gaps are prerequisite to invest in learning. In order to progress, an organization first needs a map – a skills map – to navigate and target investments.
- Temp staff providers, outsourced labor services. In some industries, such as healthcare and professional services, organizations will include contingent labor and external services as part of the solution to the lack of available labor resources.
- Marketing solutions related to candidate marketing and employer branding. In this age, the employees do not come flocking around employers. Rather, it is the other way around. Employers must target potential applicants on social media and build databases with passive candidate pools, and target these effectively. This requires marketing technology, and this opens a new target market for vendors of such solutions.
Mastering Software Cost Estimation with the New Certification and Cost estimation Body of Knowledge for Software (CEBoK-S)

Introduction
Software project failures are a harsh reality in the world of technology. Despite the best intentions and efforts, projects can unravel due to various reasons, such as poor estimation and planning, inadequate requirements gathering, scope creep, and unrealistic timelines. These failures not only result in financial losses but also tarnish a company’s reputation and erode stakeholder trust. Addressing project failures requires a proactive approach, emphasizing communication, risk management, continuous evaluation and especially realistic estimation and planning. Embracing these lessons can lead to improved project outcomes and foster a culture of learning and growth in the software development industry.
In the dynamic world of software development, accurate cost estimation is crucial to ensure project success. Organizations rely on dependable software cost estimation practices to manage budgets, meet deadlines, and deliver quality products. To address this need, a new Software Cost Estimation Certification has emerged, complemented by the Cost Estimation Body of Knowledge for Software (CEBoK-S). In this blog, we will delve into the significance of this certification and the CEBoK-S, shedding light on how they empower professionals to excel in the field of software cost estimation.
The New Software Cost Estimation Certification (SCEC)
The new Software Cost Estimation Certification is a comprehensive program designed to equip professionals with the latest tools, methodologies, and best practices for accurately estimating software project costs. Offered by the International Cost Estimation and Analysis Association (ICEAA), its special interest group ICEAA-Software, this certification reflects the industry’s evolving demands and ensures that participants stay up to date with the latest trends.
Key Components:
- Advanced Estimation Techniques: The certification program covers a wide array of advanced estimation techniques, from traditional methods like function point analysis and COCOMO to modern approaches like agile estimation and parametric modelling. By learning these techniques, professionals gain the flexibility to adapt their approach to diverse project requirements.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Effective cost estimation involves identifying potential risks and uncertainties that can impact the project’s outcome. The certification equips participants with the skills to assess and mitigate risks, allowing for better planning and resource allocation.
- Industry Case Studies: Real-world case studies are an integral part of the certification program. These case studies provide valuable insights into how cost estimation principles are applied in various scenarios, offering participants a practical understanding of the challenges they may encounter.
The CEBoK-S – Cost Estimation Body of Knowledge for Software
The CEBoK-S is a comprehensive guide that provides a structured framework for software cost estimation. Developed by industry experts, this body of knowledge encompasses a wide range of topics, from fundamental concepts to advanced practices, creating a solid foundation for professionals in the field.
Key Features:
- Detailed Framework: The CEBoK-S offers a detailed framework that covers all aspects of software cost estimation. It defines the key processes, activities, and inputs required for accurate estimation, guiding professionals through the entire estimation lifecycle.
- Best Practices and Standards: In an ever-changing industry, adhering to best practices and standards is crucial. The CEBoK-S outlines established industry standards, ensuring consistency and reliability in cost estimation practices across projects and organizations.
- Continuous Updates: Software development is continually evolving, and the CEBoK-S keeps pace with these changes. It undergoes regular updates to reflect the latest advancements and emerging trends in the field, making it a reliable and relevant resource for professionals.
Impact on the Software Industry
The combination of the new Software Cost Estimation Certification and the CEBoK-S has revolutionized the software industry’s approach to cost estimation. Certified professionals armed with the knowledge from the CEBoK-S are better equipped to address the challenges posed by modern software projects, leading to improved project outcomes and client satisfaction.
- Enhanced Project Planning: The comprehensive knowledge gained from the certification and the CEBoK-S enables professionals to create accurate and realistic project plans. This, in turn, leads to better resource allocation, reduced budget overruns, and timely project deliveries.
- Quality and Consistency: Employing standardized cost estimation practices ensures consistency in project management across different teams and organizations. This leads to higher-quality software development, as well as improved collaboration and communication among stakeholders.
- Improved Stakeholder Trust: Clients and stakeholders place their trust in organizations that employ certified professionals and follow industry standards. The certification acts as a testament to an organization’s commitment to excellence and professionalism.
- Higher success rates of software development projects, resulting in fewer cost and schedule overruns. This potentially saves companies huge amounts of money and reputation damage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the new Software Cost Estimation Certification and the CEBoK-S are instrumental in equipping professionals with the knowledge and skills required to excel in software cost estimation. By combining advanced estimation techniques with a structured body of knowledge, these resources elevate the industry’s cost estimation practices to new heights. As organizations continue to embrace these certifications, we can expect to see more successful projects, satisfied clients, and a stronger, more reliable software industry overall.
IDC Metri is proud to announce that its Software Cost Estimation Center of Excellence now has two Software Cost Estimation Certified professionals: Frank Vogelezang and Harold van Heeringen. More information can be found here: https://www.idc.com/eu/idcmetri/it-intelligence
How Can Manufacturers Transform the Customer Experience with B2B Digital Commerce
In recent years, B2B digital commerce has seen significant growth in the manufacturing sector. Manufacturers are increasingly turning to digital channels for both purchasing and sales, driven by several factors. According to our 2023 Global Manufacturing Survey, 47% of manufacturers globally consider B2B digital commerce as a strategic initiative to drive customer experience.
We talk about digital commerce as it encompasses buying and selling in digital channels and covers the different processes that also improve engagement in the customer journey, whereas eCommerce has a narrower focus on buying and selling online.
The COVID-19 pandemic acted as a catalyst for the adoption of digital commerce in manufacturing industry as digital channels provided a safe and convenient alternative, ensuring continuity in sales and procurement processes. The competitive landscape in manufacturing also requires companies to optimize costs and increase their time to market.
In an era of rapidly changing customer demands and technological advancements, manufacturers need to be agile and responsive. Furthermore, digital channels open up opportunities for manufacturers to reach new customer segments and markets.
By embracing digital commerce, manufacturers can overcome these barriers and tap into previously untapped potential.
Customer Experience is Key to Digital Commerce
In addition to the growing importance of B2B digital commerce, customer experience (CX) has become a key competitive differentiator for manufacturers globally. In the past, manufacturers focused on efficiency and product quality, but in today’s highly competitive environment, improving the customer experience has become crucial for success.
Many decision-makers involved in B2B transactions are millennials, who have grown accustomed to seamless online experiences in their B2C interactions and therefore, expect the same level of convenience and personalization in their B2B transactions. To meet these expectations, manufacturers need to provide self-service platforms that allow customers to navigate and make purchases independently.
Slow workflows and manual processes are no longer acceptable, with customers demanding on demand access to information and assistance. In response, manufacturers have embedded chat functionalities (chatbots) to provide real-time support and address any queries or concerns.
Manufacturers should also invest in designing intuitive platforms that are easy to navigate and provide a seamless buying experience. Detailed product information, along with complementary product suggestions and immersive product visualization tools, can significantly enhance CX.
How Manufacturers Can Prioritize the Customer
Delivering Personalized and Immersive Customer Experiences Through Cutting-edge Technologies
Personalization is key in B2B digital commerce. Customers expect tailored recommendations, targeted promotions, and real-time updates on order and delivery statuses. They also desire the ability to configure products and witness dynamic price changes during the buying process.
Additionally, customers increasingly prefer digital-first experiences, allowing them to make purchases anytime, anywhere, from their mobile devices.
To execute these CX initiatives successfully, manufacturers are relying on advanced analytics and artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies provide valuable insights into customer behaviors and preferences, enabling manufacturers to deliver personalized experiences at scale.
AI-powered recommendation engines, for example, can suggest relevant products based on customer browsing and purchasing history. Manufacturers are also delivering immersive experiences enabled by 3d visualization, AR/VR and other digital technologies in different phases of the buyer journey.
The customer experience does not end with the purchase. Manufacturers must have efficient processes in place to handle product returns and resolve disputes promptly. There is also an opportunity to provide additional services such as maintenance and upgrades, further enhancing the overall customer experience.
Staying Ahead of the Game Requires Continuous Innovation
In this rapidly evolving segment, manufacturers should keep an eye on emerging models and technologies. Industrial B2B marketplaces are emerging as a viable option for manufacturers to reach a broader customer base. Direct-to-customer models, which aim to establish closer relationships with customers can provide manufacturers with valuable insights on product usage and promote loyalty.
New architectures, such as headless commerce, can enable manufacturers to quickly deploy features that improve the user experience without significant infrastructure investments. This flexibility allows manufacturers to adapt and innovate at a rapid pace, staying ahead of evolving customer needs and preferences.
Connected Value Chains, Sales Empowerment, and Customer-centricity Are Key to a Successful B2B Digital Commerce Strategy
Despite the promise of B2B digital commerce, there are areas that manufacturers need to address to fully leverage their potential.
Breaking down data silos and ensuring seamless integration of digital commerce with different value chain processes is crucial. This means aligning sales and marketing efforts and integrating ERP, CRM, and other business applications with e-commerce platforms.
Manufacturers must also determine their optimal omnichannel strategy and cultivate mutually beneficial relationships with distributors to jointly create value.
The role of humans should not be overlooked in this digital transformation. Salespeople still play an important role in the B2B buying process, and their capabilities need to be augmented to align with the digital commerce landscape.
Thanks to digital commerce, sales reps are no longer burdened by time consuming tasks and can focus on other activities such as guiding customers through the buying process for more complex orders. Empowering salespeople with readily available information and insights can enhance their interactions with customers and drive sales.
Finally, building an organization-wide culture based on customer centricity is vital for manufacturers. Putting the customer at the center of decision-making across all organizational functions ensures that CX remains a top priority and drives continuous improvement.
The IDC Manufacturing Insights: Worldwide Manufacturing B2B Commerce and Customer Experience Technology Strategies subscription service analyses the key trends in B2B digital commerce and how manufacturers are creating value and delivering innovative customer experiences by leveraging digital technologies. Reach out to me at mcasidsid@idc.com to learn more about this new program.
How Retailers and Brands are Taking Advantage of Generative AI?
Is GenAI the “Next Big Thing” in Retail?
The retail industry is moving fast. Evolving customer expectations and needs, fierce competition, and the quest for enhanced online customer experience – among others – are all factors driving retailers to rush into experimenting with emerging technologies. In 2022, newspapers were crowded with titles of bold retailers and brands landing in the Metaverse; 2023 has already proved to be the year of Generative AI (GenAI).
Following the hype, in the last months we have seen the web crawling with OpenAI’s DALL-E experiments, an example is the viral AI-generated video series “By Balenciaga”, or the ultra-realistic image of Pope Francis wearing a Moncler puffy jacket. However, the potential applications of the technology in the retail industry are much more tangible than digital content creation for mere customers’ entertainment.
GenAI technologies (such as ChatGPT and Dall-E), and solutions powered by LLMs, or text-to-image models are publicly set to have a disruptive impact across all retail operations and functions. The expected benefits of the technology span from enhancing and accelerating retailers marketing creative process to achieving the personalization of online customer journeys based on individual preferences and needs.
How Are Retailers Approaching Generative AI Nowadays?
With the OpenAI release of ChatGPT in early November 2022, large language models (LLMs) or foundation models (FMs) become available to the general public, and everyone had the chance to experience firsthand their transformative power in terms of augmenting human productivity and creativity- retailers included.
According to our findings, 40% of worldwide retailers and brands are in the experimentation phase of GenAI, trying to figure out the most relevant field of applications and use cases, while 21% are already investing in the implementation of GenAI technologies. Today we see organizations such as Coca-Cola, Mattel, and Carrefour starting to pilot GenAI applications, even if still on a limited scale and with a test-and-learn approach, predominantly across the areas of product development, marketing, and customer service.
Download eBook: Generative AI in EMEA: Opportunities, Risks, and Futures
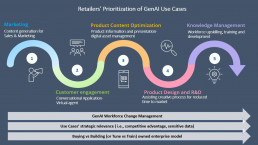
Which GenAI Use Cases Do Retailers Expect to Explore in the Short Term?
In the short-term, most retailers expect to explore LLMs and FMs applications in marketing, sales and customer engagement, as confirmed by our data showing that 50% of them will prioritize GenAI marketing use cases over the next 18 months. Knowledge management, design and conversational applications are following marketing in the current retailers’ prioritization of GenAI use cases, while code applications are lagging for the moment- as opposed to other industries where they are leading the way for the technology implementation.
Unsurprisingly, retailers are starting to approach GenAI through less strategic and data-sensitive use cases using open-source commercial models or plug-in solutions (i.e., marketing and conversational applications). Other more strategic retail use cases (i.e., product prototyping and knowledge management) would require the fine-tuning of commercial models to the organization dataset and eventually the training of their own proprietary model or enterprise solution.
Therefore, we could expect these strategic use cases to reach wide adoption in the medium-long term- when the technology will become more established, and retailers will have developed enhanced GenAI in-house capabilities and workforce change management.
How Will GenAI Impact the Retail Industry?
We define Generative AI as a branch of computer science that involves unsupervised and semi-supervised algorithms that enable computers to create new content using previously created content, such as text, audio, video, images, and code in response to short prompts. Therefore, the power of GenAI goes beyond chatbots and lies in its ability to create infinite, contextualized content of any format.
Theoretically, the Retail industry could see significant improvements when advanced GenAI’s content creation ability will be added on top of the existing AI/ML applications that retailers use to automate processes, enhance personalization, and increase efficiency- and across all retail functions.
In the short-term, even if the technology will inevitably raise important questions in terms of proprietary data sharing, customer data privacy, and factual inaccuracy, without any doubt the integration of GenAI into online customer journeys could lead to significant improvements in both the backend of e-commerce workflows and the front-end of online customer experience– leading to major enhancements in retail e-commerce efficiency and efficacy.
The disruptive power of GenAI for digital commerce is not going unnoticed, for instance, the Chinese e-commerce giant JD.com announced the imminent release of its own retail-specific ChatGPT solution which aims to improve online retailers’ rankings of product listing on SERP, generate product descriptions that are tailored to a shopper’s preferences, and optimize online product images and video generation process.
Watch the Webcast: Generative AI in EMEA: Opportunities, Risks, and Futures
Two Nascent GenAI Use Cases with Examples
Conversational Customer Service Chatbots: Carrefour
Compared to the standard chatbots that are typically limited by a defined number of interactions and decision trees, GenAI conversational applications open an infinite number of responses to potential customers’ inquiries. In doing so, the GenAI virtual assistant can provide more inspirational bits of advice, guiding the shoppers throughout the whole website navigation journey with contextual and relevant information about the product listed in their vast online catalogue.
In the short term, conversational AI could be an attractive option for retailers in need of powering up their poor e-commerce search experience, as it could be easily done by plugging in GenAI solutions through API rather than reviewing their in-house search capabilities. Ultimately, GenAI could lead to a different kind of product search, giving shoppers the chance of starting a conversation with the retailer/brand by uploading an image, photo, and audio, or by simply speaking to the intelligent AI concierge.
For example, starting from June 8, French grocery retailer Carrefour has integrated a chatbot based on ChatGPT into its company website, giving shoppers the ability to use natural-language AI to assist them in their daily grocery shopping. Customers can find “Intelligent Assistance” on the company home page and consult it in choosing the best products based on their budget, food intolerances and allergies, or even specific menu ideas.
Also, being connected to Carrefour’s website research engine, the chatbot can give a real-time list of products while conversing with customers until the purchase is finalized.
Enhanced Product Visualization Online: Anthropologie, Everlane, H&M and LOFT
Product visualization online has been historically the main source of frustration for shoppers and forgone sales for retailers, especially when the product in question is an experiential one such as a piece of clothing or furniture. Using GenAI for image generation, retailers and brands can optimize the creation of product images, reducing the time and costs associated with in-studio shooting. Indeed, GENAI tools can be used to transform text or 2D images into 3D products representation to offer more appealing and interactive online product catalogues.
H&M, LOFT, Everlane and Anthropologie – among other brands – are all partnering with Google in its latest release of a GenAI virtual try-on tool for women’s apparel on Search. Starting from the brand product catalogue image, the tool can create in real-time an AI-Generated rendering of how it would fit on a diverse set of real models in various poses.
Concerning other previous attempts at virtual try-ons for clothes, such as the AR-powered “Be Your Own Model” released by Walmart, GenAI technology is raising the bar by reflecting accurately how articles of clothing drape, fold, cling, stretch and form wrinkles and shadows- and do it at scale.
GenAI in Retail: What’s Next?
LLMs, FMs and GenAI advancements are happening quickly, especially in comparison to more slow-burn technologies that we have seen emerging in the previous years- such as metaverse, blockchain or AR (Augmented Reality) and VR (Virtual Reality). The immediate applications for the retail industry that we have seen above suggest that retailers and brand executives must start planning their GenAI strategy today, since many of the use cases that might seem so futuristic now could become viable within months rather than years.
In this context, a wait-and-see approach could be risky for retailers. Therefore, they must start experimenting with a test-and-learn approach now to develop a repeatable process that can be deployed tomorrow on a larger scale, while setting the basis in the workforce for GenAI change management and in-house capability building.